Subspecialty trained pediatric anesthesiologists are medical professionals who specialize in providing anesthesia and perioperative care to infants, children, and adolescents. This subspecialty requires extensive training and expertise due to the unique physiological, psychological, and developmental considerations involved in treating pediatric patients.
The Importance of Subspecialization in Pediatric Anesthesia
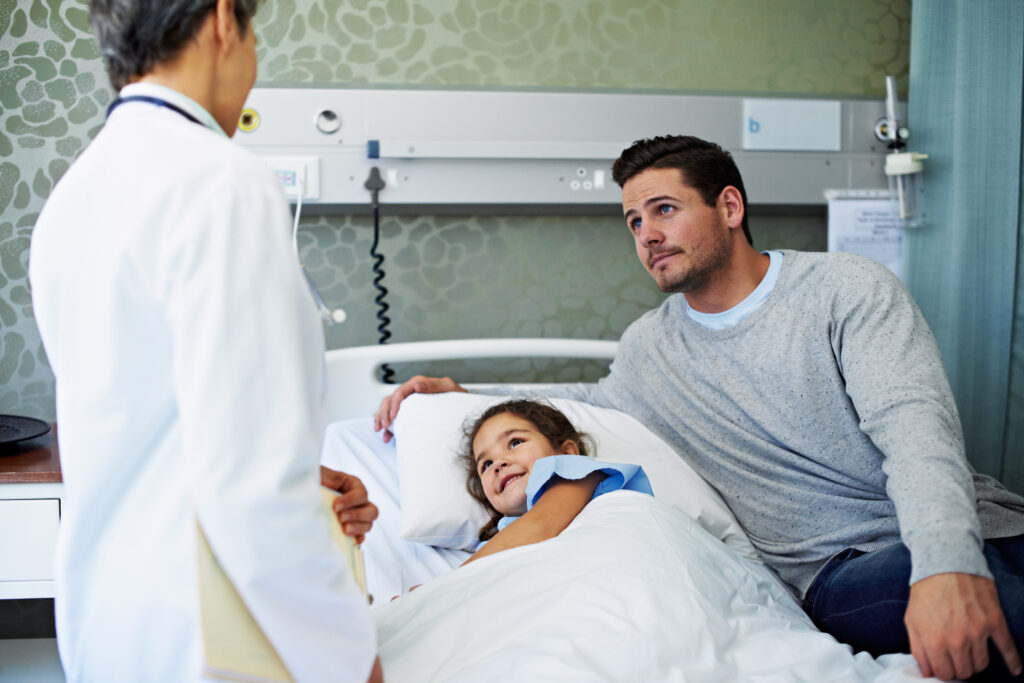
Pediatric anesthesiology is a highly specialized field that recognizes the distinct needs of children in the perioperative environment. Children are not just small adults; they have different anatomical, physiological, and emotional needs that must be expertly managed during surgical procedures. Pediatric anesthesiologists are equipped to handle these unique challenges, ensuring the safety and comfort of their young patients.
Training and Qualification
Becoming a subspecialty trained pediatric anesthesiologist involves several years of additional training beyond the standard medical education and general anesthesiology residency. This includes a fellowship in pediatric anesthesia, where physicians gain specialized knowledge and experience in managing infants, children, and adolescents. This training covers a wide range of topics, including neonatal anesthesia, pain management in children, and handling emergencies in pediatric patients.
Expertise in Pediatric Physiology and Pharmacology
Children’s bodies respond differently to anesthesia and medications compared to adults. Pediatric anesthesiologists have a deep understanding of these differences. They are trained in the pharmacokinetics (how drugs move through the body) and pharmacodynamics (how drugs affect the body) specific to pediatric patients. This knowledge is crucial for determining appropriate drug dosages and managing potential side effects.
Managing Emotional and Psychological Aspects
Anesthesia can be a frightening experience for a child. Pediatric anesthesiologists are skilled in communicating with children and their families, helping to alleviate fears and anxieties. They often employ various techniques, such as distraction or the use of child-friendly language, to make the experience less intimidating for young patients.
Intraoperative Care
During surgery, pediatric anesthesiologists are responsible for maintaining the child’s vital functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. They monitor the child’s response to anesthesia and adjust it as needed. This requires a keen understanding of the physiology of growing bodies and the ability to quickly respond to any changes in the child’s condition.
Pain Management
Effective pain management is a critical aspect of pediatric anesthesia. Pediatric anesthesiologists are experts in assessing and managing pain in children, who may not always be able to communicate their discomfort effectively. They use various methods, including medications and nerve blocks, to ensure that their patients are as comfortable as possible both during and after surgery.
Special Considerations for Neonates and Young Infants
Neonates and young infants pose additional challenges due to their underdeveloped organs and systems. Pediatric anesthesiologists are specially trained to manage these vulnerable patients, understanding the subtleties of administering anesthesia to this population and the implications for their developing bodies.
Anesthesia for Chronic Conditions and Special Needs
Children with chronic medical conditions or special needs require tailored anesthetic care. Pediatric anesthesiologists are experienced in managing patients with a wide range of conditions, from congenital heart disease to developmental disorders, ensuring that their specific medical needs are met during surgery.
Research and Advancements
Subspecialty trained pediatric anesthesiologists are often involved in research to improve anesthesia care for children. This includes developing new techniques, refining drug protocols, and investigating the long-term effects of anesthesia on pediatric patients. Their contributions are vital to advancing the field and improving outcomes for young patients.
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Professionals
Pediatric anesthesiologists work closely with pediatric surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care. This teamwork is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of pediatric patients throughout the surgical process.
Conclusion
Subspecialty trained pediatric anesthesiologists play a critical role in the healthcare of children. Their extensive training and expertise allow them to provide specialized care that meets the unique needs of pediatric patients. From managing the physiological and pharmacological aspects of anesthesia to addressing the emotional and psychological needs of children, these professionals ensure that young patients receive the safest and most effective perioperative care possible. Their dedication and skills are indispensable in the realm of pediatric healthcare, making a significant difference in the lives of children and their families.